EMG album [1] Introduction to EMG
2019-06-10
Today for a change, let's understand the definition of electromyography and related detection techniques.
I. What is EMG?
Electromyogram (EMG) is a method to record the electrical characteristics of muscle during rest, voluntary contraction and peripheral nerve stimulation. EMG is an extension of clinical physical examination.
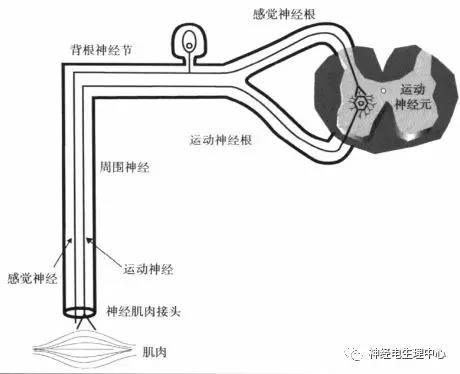
2. What are the EMG detection techniques?
In the narrow sense, electromyography (EMG) usually refers to the recording of various electrical characteristics of resting and voluntary contraction of muscles by using the same core round needle electrode.
The broad electromyogram package includes examinations related to peripheral nerves, neuromuscular junctions (NMJ) and other electrodiagnostic examinations of muscle diseases. Common detection techniques include:
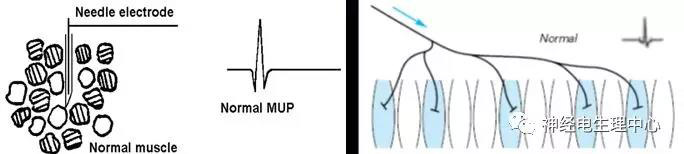
(1) needle electromyogram (EMG)
A. Electromyogram of the same core round needle electrode
B. Single fiber electromyogram (SFEMG)
C. Maco-EMG
針電極檢測:
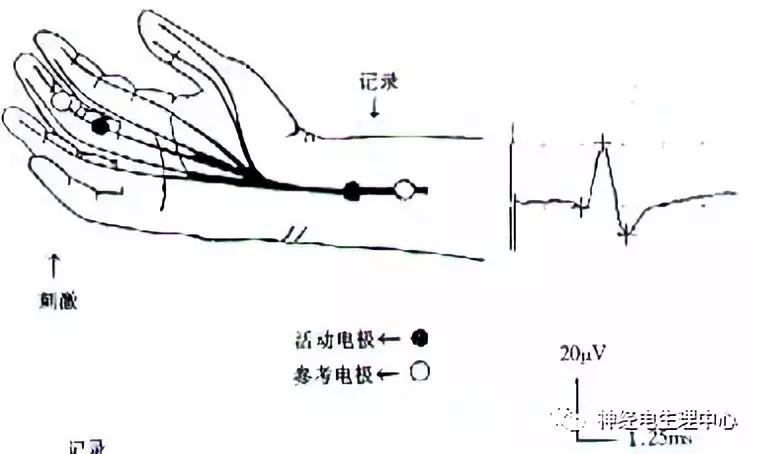
(2) Nerve conduction study , NCS: limb nerve, cranial nerve, pudendal nerve, etc.
Nerve conduction test:
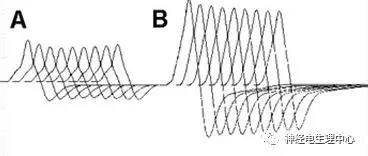
(3) Repetitive nerve stimulation , RNS
(4) F wave
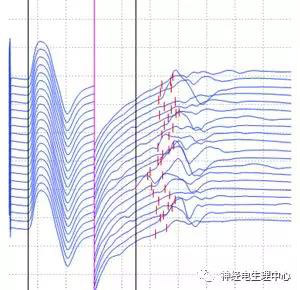
(5) H reflex
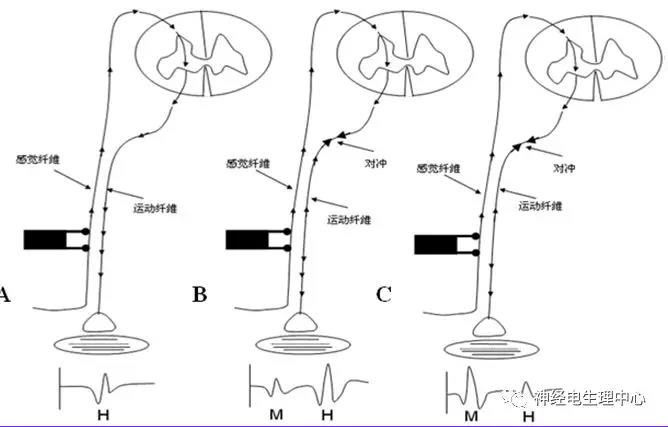
(6) Blink reflex , BR
Blink reflection waveform:

(7) Evoked potential , EP
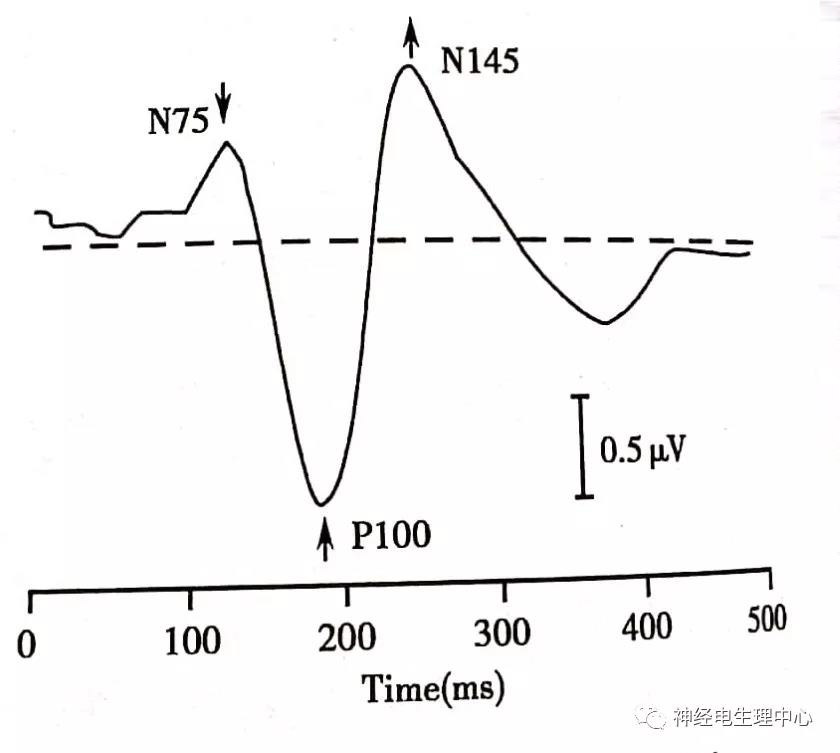
a.Visual evoked potential , VEP
Visual evoked potential waveform:
b.Brainstem auditory evoked potential , BAEP
Brainstem auditory evoked potential waveform:

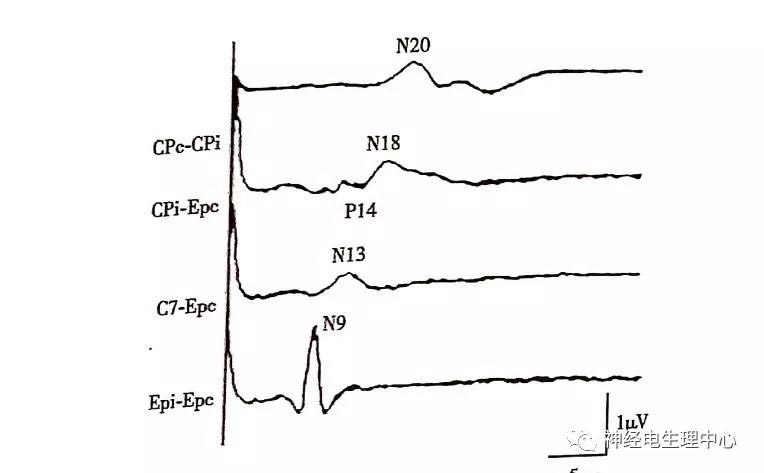
c.Somatosensory evoked potential: the most commonly used is short latency somatosensory evoked potential(short latency somatosensory evoked potential , SSEP)
Upper limb somatosensory evoked potential waveform:
3. What does EMG do?
To provide localization diagnosis and differentiation for anterior horn cells of spinal cord and/or motor nucleus of brainstem and its following parts, including localization diagnosis of anterior horn cells of spinal cord, nerve root, nerve plexus, peripheral nerve, neuromuscular junction and muscular lesion sites; to guide the selection of injection sites of intramuscular drugs (such as botulinum toxin or other drugs).
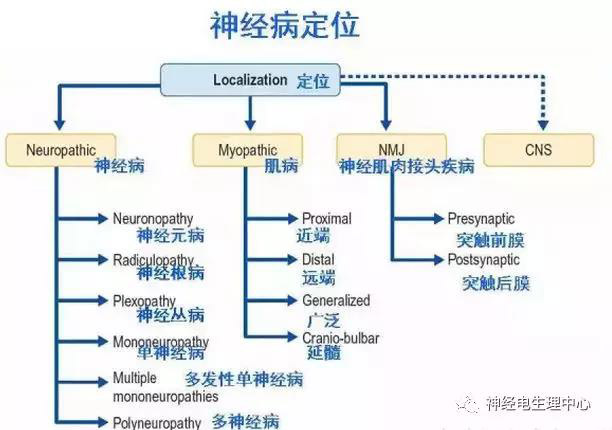
4. Who needs EMG examination?
Nerve conduction detection and needle electromyography are most commonly used in the diagnosis of peripheral neurological diseases. Among the common patients, most of the symptoms can be summarized in simple sixteen words: limb weakness, numbness of hands and feet, muscle atrophy, nerve injury. And other symptoms associated with testing techniques.
Through the above introduction, we have a general understanding of the definition of EMG, common detection techniques and examination purposes. In future articles, various inspection techniques mentioned above and some other new technologies will be introduced in detail.
Reference:
1. Revised Consensus on Normalized Detection and Clinical Application of EMG (2015) - Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Association
2. Easy Learning EMG (America) - Translated by Pan Hua
3. Diagnosis and Clinical Application of EMG - Dang Jingxia



